"""
===============================
Using geometric transformations
===============================
This example illustrates use of geometric transformations in the context of
image processing.
"""
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skipp import transform
######################################################################
# Basics
# ======
#
# Affine geometric transformation is supported.
#
# Geometric transformations can either be created using the explicit
# parameters (e.g. scale, shear, rotation and translation) or the
# transformation matrix.
#
# Create a transformation using explicit parameters:
tform = transform.AffineTransform(scale=1, rotation=math.pi/2,
translation=(0, 1))
print(tform.params)
######################################################################
# Alternatively, define through a transformation matrix:
# itself:
matrix = tform.params.copy()
matrix[1, 2] = 2
tform2 = transform.AffineTransform(matrix)
######################################################################
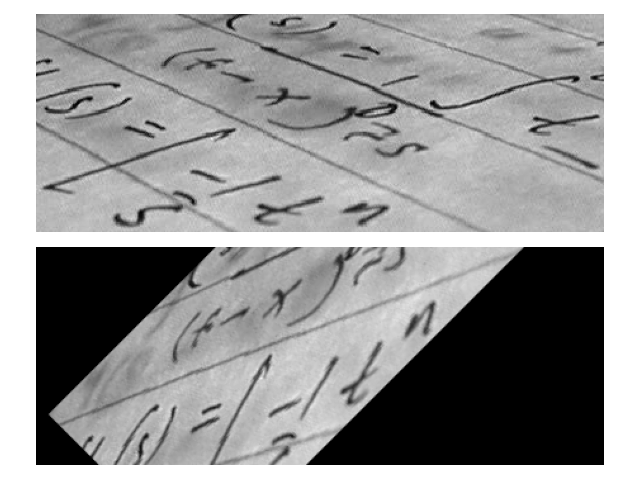
# Image warping
# =============
#
# Geometric transformations can also be used to warp images:
text = data.text()
tform = transform.AffineTransform(scale=1, rotation=math.pi/4,
translation=(text.shape[0]/2, -100))
rotated = transform.warp(text, tform)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=2)
ax[0].imshow(text, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[1].imshow(rotated, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
for a in ax:
a.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()